Standards for Low-Voltage Electrical Installations
Regulation and standardization
What is regulation?
These are texts published by the administrative authorities of a state resulting from a law or regulation. They are mandatory. Generally, these texts define the essential requirements relating to areas such as the environment, safety (health, industrial, food, work…), bioethics …
For EU member states, part of the regulation comes from the transposition of EU directives.
What is standardization?
Standards are documents developed by a recognized standardization body. In general, standards are not mandatory. Compliance with the standard is a presumption of regulatory compliance.
All or part of certain standards may be made mandatory in the regulations in order to simplify their content.
The vast majority of standards relate to products. Nevertheless, the field of electrical installations is subject to substantial standardization.
The four categories of standards
There are four categories of standards:
- International standard: a standard adopted by an international standardization body;
- European standard: a standard adopted by a European standardization body;
- Harmonized standard: a European standard adopted on the basis of a request by the European Commission for the application of EU harmonization legislation;
- National standard: a standard adopted by a national standardization body.
International standardization bodies
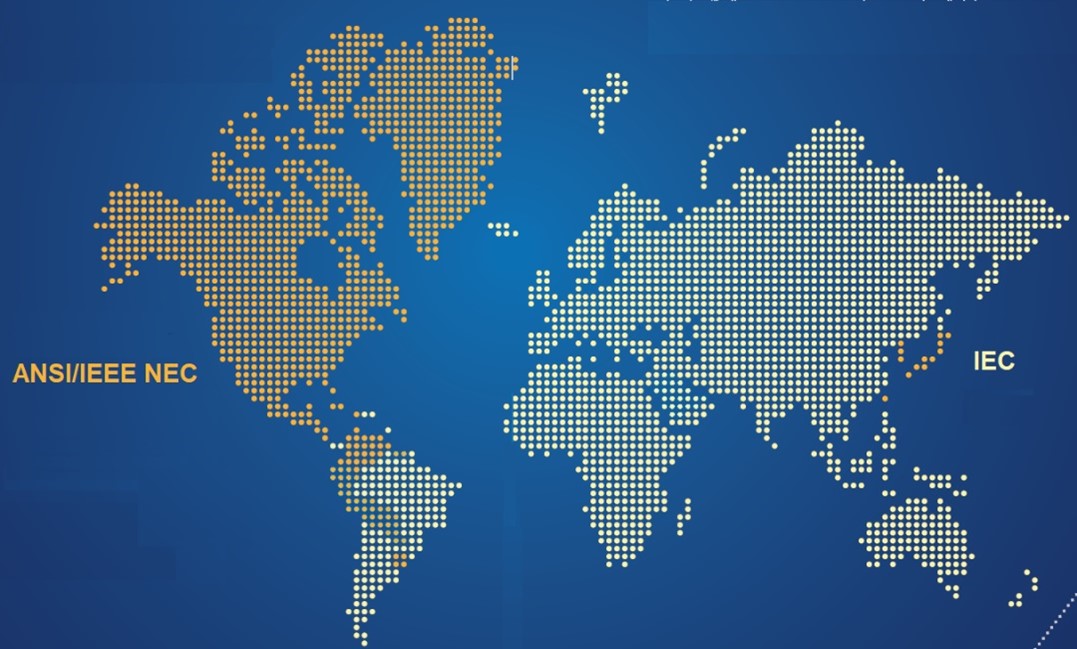
At the international level, there are two major standardization bodies relating to the electrotechnical engineering field and electrical installations in particular:
ANSI/IEEE NEC: The standards developed by these bodies are used mainly in North America, Central America, and some South American countries with some national deviations, as well as in the Philippines.
IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission): It can reasonably be said that countries that do not use the ANSI/IEEE NEC standards refer to the IEC standards. This body claims 173 affiliated countries.
The European Standardization Body
CENELEC (European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization): This body is made up of 34 member countries that are represented by their national standardization bodies. All EU countries are of course part of CENELEC. In addition, 13 other countries participate in CENELEC’s work as “Affiliates” or “Companion Standardization Bodies”.
CENELEC’s national members have a responsibility to implement European standards as national standards. National standardization bodies distribute the implemented European standards and must remove any national standard in conflict.
Cooperation between the IEC and CENELEC is very close. It is materialized by the Frankfurt Agreement. For more than 20 years, new electrical standards projects have been jointly planned by CENELEC and IEC, and, where possible, most are carried out internationally. As a result, almost 80% of CENELEC standards are identical or based on IEC publications. This is particularly the case for low-voltage electrical installations.
For low voltage electrical installations, the CENELEC series of standards that corresponds to IEC 60364 is the HD 384 series. The prefix HD means that this set of standards is part of the harmonization legislation of the European Union. HD 384 standards are exactly the same as IEC 60364.
National Standardization Bodies
Most countries re-transcribe the various IEC 30364 or HD 384 standards in their national standardization systems depending on their affiliation. Some variations may be introduced at the time of this transcript to reflect the history. But for CENELEC members, under no circumstances should a particular requirement conflict with the transcribed standard.
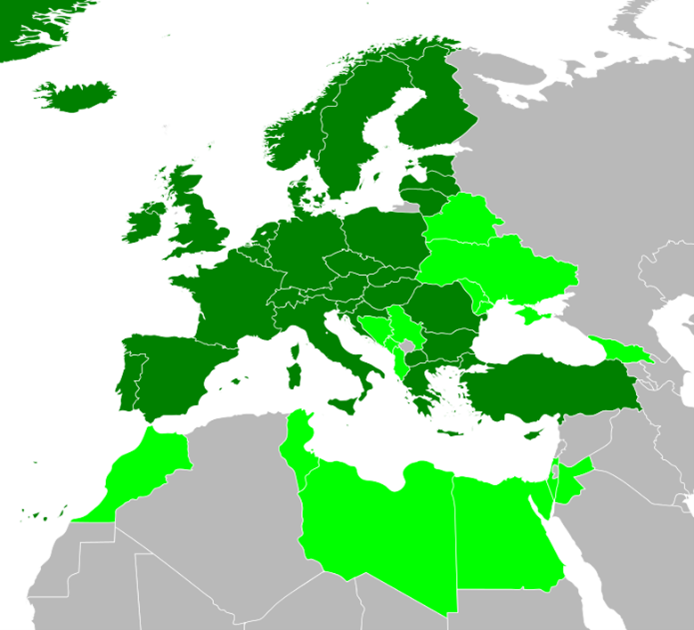
Given their historic agreements, some countries use another country’s national standards. This is particularly the case with the French NF C 15-100 standard, which is used in some African countries, or the British standard BS 7671, which is used in some countries in Africa or the Middle East.
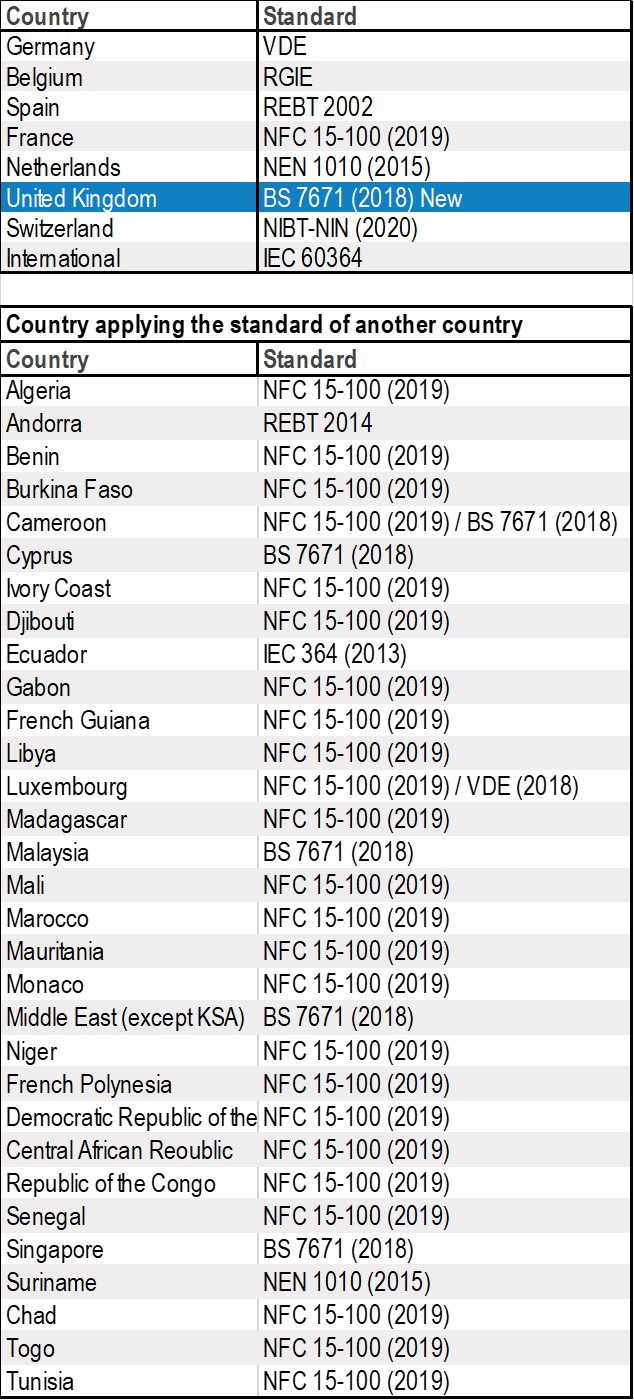
Electrical standards available in elec calc™
The following table specifies the electrical standards implemented in the elec calc™ software as well as third countries that also use these national standards.
Reminder of the structure of the IEC 60364 / HD 384 standards
Part 1: Fundamental principles, assessment of general characteristics, definitions.
Part 4: Protection for safety
• Section 41: Protection against electric shock
• Section 42: Protection against thermal effects
• Section 43: Protection against overcurrent
• Section 44: Protection against electromagnetic and voltage disturbances
Part 5: Selection and erection of electrical equipment
• Section 51: Common Rules
• Section 52: Wiring systems
• Section 53: Isolation, switching and control
• Section 54: Earthing arrangements
• Section 55: Other equipment
• Section 56: Safety services
Part 6: Verification
Part 7: Requirements for special installations or locations (This part includes requirements for specific installations such as photovoltaic installations, charging facilities for electric vehicles, outdoor lighting…)
Part 8: Functional aspects (The energy efficiency aspect is dealt with in this part)